In this article, we will learn how to calculate the number of hours per month, allowing for daylight-saving shifts in Microsoft Excel 2010.
To calculate the number of hours per month, allowing for daylight-saving shifts, we will use a combination of DAY, EOMONTH & DATE functions to get the output.
DAY: Returns the day of the month, which is a number from 1 to 31
Syntax: =DAY(serial_number)
serial_number: It refers to the day of the month that you are trying to find.
EOMONTH: This function is used to calculate the last day of the month. EOMONTH can be used to calculate maturity dates or due dates that occur on the last day of the month.
Returns the serial number of the last day of the month before or after a specified number of months.
Syntax: =EOMONTH(start_date,months)
DATE: Returns the number that represents the date in Microsoft Excel date-time code.
Syntax: =DATE(year,month,day)
year: The year argument can include one to four digits. By default, Excel uses the 1900 date system.
month: The second argument representing the month of the year from 1 to 12 (January to December)
day: The third argument representing the day of the month from 1 to 31.
Let us take an example:
With below formula we will be able to subtract 1 hour from April month & add to October month.

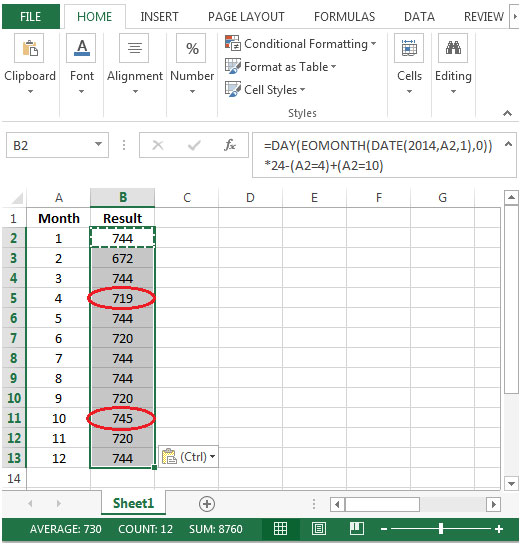
You will notice the number of hours in month of April have been reduced by 1 & for month of October, 1 hour has been added to total work hours.
The applications/code on this site are distributed as is and without warranties or liability. In no event shall the owner of the copyrights, or the authors of the applications/code be liable for any loss of profit, any problems or any damage resulting from the use or evaluation of the applications/code.