In this article, we will be learning why #N/A occur And How to Fix #N/A in Excel.
In excel, at times we get #N/A error. This error occurs when there is something important missing with something which can't be found or identified in the formula you have supplied to the cell and is recognized by Excel by showing the error. As per Microsoft official site a #N/A is Excel's way of saying, the value you are looking for is not available in the list you provided.
If you are looking for some value in the table and if it can't be found or identified, this error suggests you to check some points discussed below.
Let’s understand how this error occurred and how to fix them with some examples
The most basic reason of #N/A error is when cell value is not found in the list. Generally Excel matches the value with each element of the lookup array and returns the first matched value if found or else it returns #N/A error. Here #N/A error suggests that Value you are looking for in the list is not found. See the below example to understand more.
For example, LOOKUP function matches the value in the first array and returns value from the corresponding second array. In the data shown below.
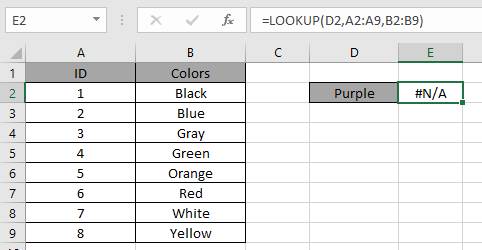
Look in the above snapshot and realize the mistake just happened. The above function looks for the value "Purple" in the ID column which obviously it won't be able to find.
How to fix it! You cannot fix the error for the result if there's no matched value in the result. But the first problem here is that we are looking at the wrong array. Check the array that you are giving as an argument to the function.
two ways to catch this error which returns the #N/A Error
First method is via Using IFERROR function to catch the error by the function
Generic formula:
| = IFERROR ( FUNCTION , "response" ) |
Explanation:
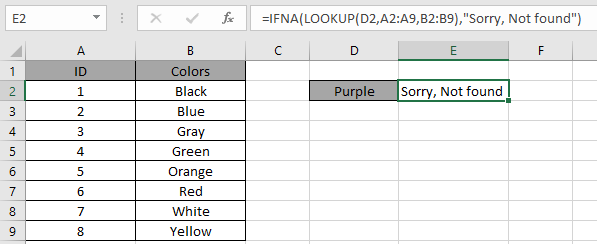
In the above snapshot the function returns the response "Sorry, not found" instead of the error.
The second method is via the IFNA function to catch the error by the function. This function is exclusively made to catch the #N/A error.
Generic formula:
| = IFNA ( FUNCTION , "response" ) |
Explanation:
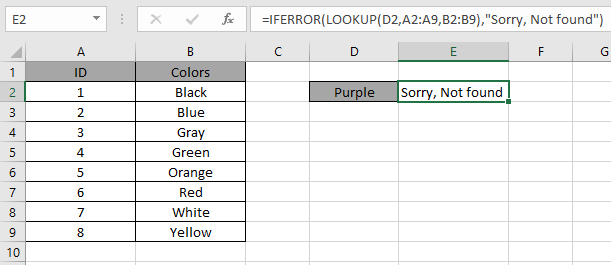
In the above snapshot the function returns the response "Sorry, not found" instead of the error.
As you can see the #N/A Error can be handled when operating with functions.
#N/A error due value not identified
The most basic reason of #N/A error is when cell value not identified in the list. Generally Excel matches the value with each element of the lookup array and returns the first matched value if found or else it returns #N/A error. Here #N/A error suggests that Value you are looking in the list is not identified. See the below example to understand more.
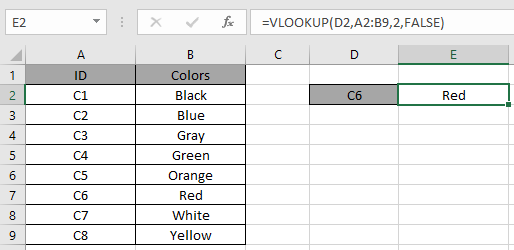
For example, LOOKUP function matches the value in the first array and returns value from the corresponding second array. In the data shown below.

Look in the above snapshot and realize the mistake just happened. The above function looks for the ID "C6" in the ID column which is marked in RED box. So why the function is not giving the output.
How to fix it! You can fix this error for the result, follow the points shown below.
In the above snapshot there was an error with extra space.
As you can see the #N/A Error can be handled when operating with functions.
two ways to catch this error which returns the #N/A Error
First method is via Using IFERROR function to catch the error by the function
Generic formula:
| = IFERROR ( FUNCTION , "" ) |
Explanation:

In the above snapshot there was an error with extra space.
As you can see the #N/A Error can be handled when operating with functions.
two ways to catch this error which returns the #N/A Error
First method is via Using IFNA function to catch the error by the function
Generic formula:
| = IFNA ( FUNCTION , "" ) |
Explanation:

In the above snapshot the function returns the empty string ( "" ) as response instead of the error.
Trapping #N/A error with INDEX and MATCH function
IF using the INDEX and MATCH function instead of VLOOKUP function. See the below snapshot and the formula used in the table. Use the formula.
| = IFERROR ( INDEX ( B2:B9 , MATCH ( D3 , A2:A9 , 0 ) ) , "Not found" ) |
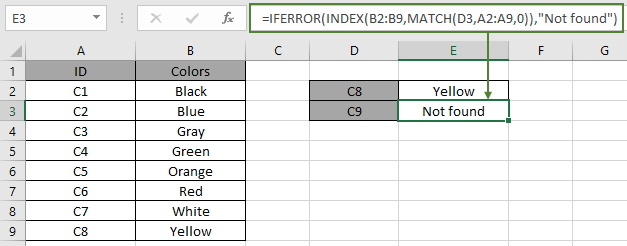
As you can see how #N/A error with function returns #N/A error and after the correction the formula works fine.
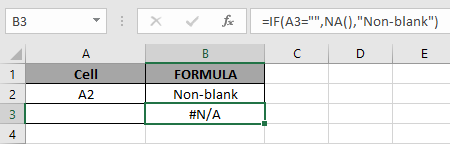
In excel, you can force the #N/A error if no need to display as the result. Using the NA function of Excel.
Use the formula:
| = IF ( A3 = "" , NA() , "Non-blank" ) |
Hope this article about how Why #N/A occur And How to Fix #N/A error in Excel is explanatory. Find more articles on Excel errors functions here. Please share your query below in the comment box. We will assist you.
Related Articles
#VALUE Error And How to Fix It in Excel
How to Remove Text in Excel Starting From a Position
Create drop down list in excel with colour
Remove leading and trailing spaces from text in Excel
Popular Articles
If with conditional formatting
Join first and last name in excel
Count cells which match either A or B
The applications/code on this site are distributed as is and without warranties or liability. In no event shall the owner of the copyrights, or the authors of the applications/code be liable for any loss of profit, any problems or any damage resulting from the use or evaluation of the applications/code.