In this article, we will learn How to create a Table and name the table in Excel.
Scenario :
While working on Excel, you’ve must have heard about named ranges in excel. Maybe from a friend, colleague or some online tutorial. I have mentioned it many times in my articles. In this article we will learn about Named Range in Excel and will explore each and every aspect of it.
What are Named tables in Excel?
Well, named ranges are nothing but some excel ranges that are given some meaningful name. For example if you have a cell say B1, containing everyday targets, you can name that cell as specifically “Target”. Now you can use “Target” to refer at A1 instead of writing B1.
In a nutshell, Named range is just naming of ranges.
How to name a range in Excel?
Define name manually:
To define a name to a range you can use shortcut CTRL + F3. Or you can follow these steps.

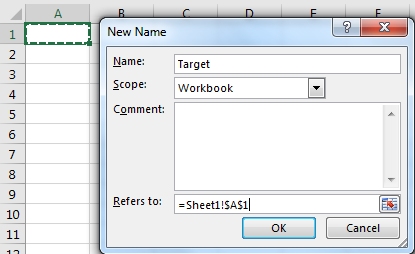
Now you can refer to it by just typing its name.
There are some rules to follow while creating names. Here are some.
Define name Automatically
Well most of the time you will be working with structured data tables. They will have column and rows with column headings and row headings. And most of the time these names are meaningful to the data and you’d like to name your range as these column headings. Excel provides a tool to automatically name ranges using headings. Follow these steps.
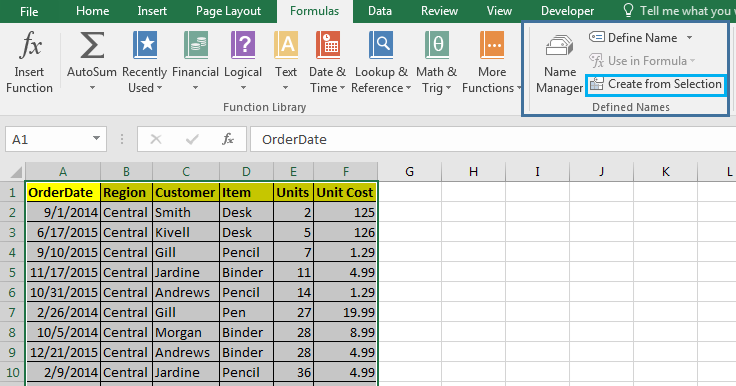

Now each column is named as their heading. Whenever you type a formula, these names will be listed as options which can be accessed.
Naming Range Using Excel Tables
When we tablise a data in excel using CTRL + T, the column heading automatically is assigned as the name of the respective column. You should explore Excel Tables and their benefits.
How to See All Named Ranges?
Well there will be times when you would like to see all available named ranges in the workbook. To see all name ranges Press CTRL+F3. Or you can go to Formula Tab > Name Manager. This will list all named ranges that are available on the workbook. You can Edit available named ranges, delete them, add new names.
One Range Multiple Names
Excel allows users to name the same range with different names. For example range A2:A10 can be named ‘Customers’ and ‘Clients’ both at same time. Both names will refer to the same range A2:A10.
But you can’t have the same names for two different ranges. This is good. This eliminates the chance of ambiguity.
Get List of Named Ranges on Sheet
So if you want to have a list of named ranges and the ranges they are covering you can use this shortcut for pasting them in place in a sheet.


If you double click on the named ranges name in the paste name box, they will get written as formulas in the cell. Try it.
Update Named Ranges Manually
Well when you insert a cell inside a named range it updates automatically and expands it. But if you add data at the end of the table, you’ll need to update the named range. To update Named Ranges follow these steps.
And It's done. This is manual updating of named ranges. However, we can make it dynamic by using some formulas.
Update Named Ranges Dynamically
It is wise to make your named ranges dynamic so that you don’t have to edit them whenever your data overflows the predefined range.
I have covered it in a separate article called Dynamic Named ranges. You can learn and understand the benefits of it in detail here.
Deleting Named Ranges
When you delete the sum part of the named range, it auto adjusts its range. But when you delete the whole name range vanishes from the name list. Any formula, dependent on those ranges will show #REF error or they will give incorrect output (counting functions).
For any reason, if you want to delete named ranges, just follow these steps.

Caution: Before you delete the named ranges make sure that no formulas are dependent on these names. If there is any, convert them to ranges first. Otherwise you’ll see #REF error.
Deleting Names with Errors
Excel provides tools to delete names that have errors only. You don’t need to identify each of them by yourself. To delete names with errors, follow these steps:
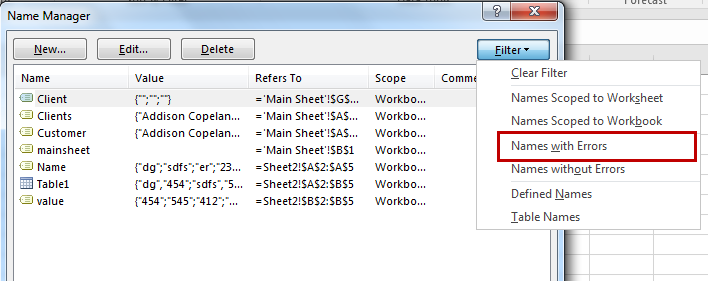 Select All and hit the delete button.
Select All and hit the delete button.And they are gone. All the names with errors will be deleted from record immediately.Named Ranges With Formulas
Best use of named ranges are explored with formulas. The Formulas get really flexible and readable with Named ranges. Let’s see how.
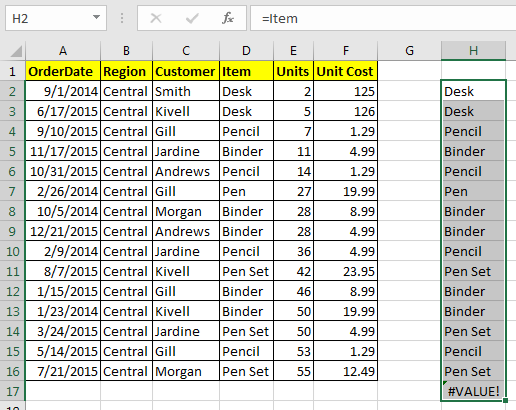
Easy To Write FormulasNow let’s say you have named a range as “Items”. Now the Items list you want to count “Pencils”. With names it is easy to write this COUNTIF formula. Just write
=COUNTIF(Item,"Pencil")
As soon as you write the opening parenthesis of formula the list of available named ranges will appear
Without name you would write a give a range to COUNTIF function of Excel, for which you may have to look at the range first then select the range or type it in formula.Excel Serves the Available Name Ranges.
The named ranges are shown as suggestions when you type any letter. As excel shows the list of formulas. For example if you type =u, each formula and named range will be displayed starting with u, so that you can use them easily.

Make Constants using Named Ranges
So far, we learned about naming ranges but you can actually name values too. For example if your client name is Sunder Pichai then you can make a name “Client” and it refers to write “Sundar Pichai”. Now whenever you will write =Client in any cell it will show Sundar Pichai.
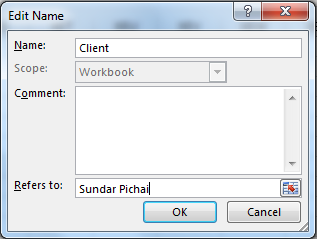

Not only text, but you can also assign numbers as constant to work with. For example, you define a target. Or the value of something that will not change.
Absolute and Relative Referencing with Named Ranges
The referencing with Named ranges in is very flexible. For example if you write the name of a named range in a relative cell to the named range, it will behave like a relative reference. See below image.
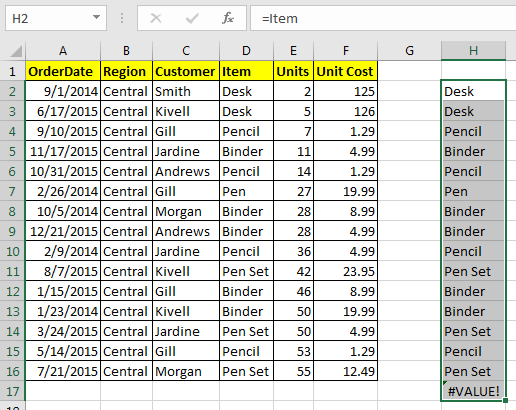
But when you use it with formulas it will behave as absolute. Well most of the time you’ll be using them with formulas, so you can say that they are by default Absolute but actually they are flexible.
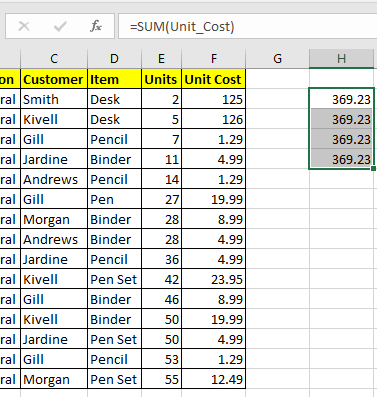
But we can make them relative too.
How to make Relative Named Ranges in Excel?
Let’s say if i want to name a range “Befor” which will refer to cell left to wherever it is written. How do I do that? Follow these steps:
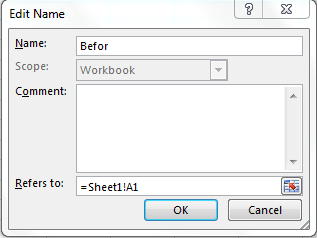
Now wherever you will write the “Befor” in formula, it will refer to cell left to it.

Here, I used it before in the COLUMN function. The formula returns the column number of the left cell where it is written. To my suprise, A1 shows the column number of the last column. Which means the sheet is circulare. I thought it will show an #REF error.
Give Name to Often Used Formulas?
Now this one is amazing. Many times you use the same formula again and again in a worksheet. For example you may want to check if a name is in your customer list or not. And this need may occur many times. For this you’ll write same complex formula every time.
| =IF(COUNTIF(Customer,I3),"In List","Not in List") |
How about, if you just type ‘=IsInCustomer’ in a cell and it will show you if the value in the left cell is in the customer list or not?
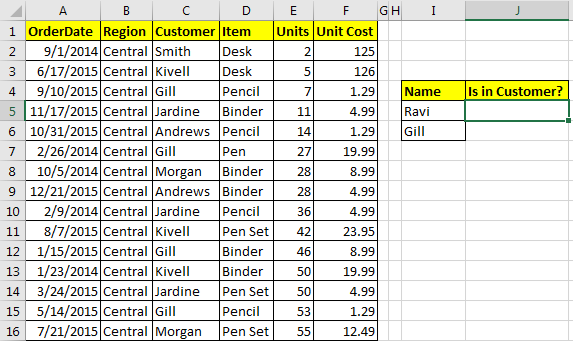
For example, I have prepared a table here. Now i just want to type “=IsInCustomer” in J5 and i would like to see if the value in I5 is in the Customer list or Not. To do so follow these steps.
In ‘Refers To’ write your formula. =IF(COUNTIF(Customer,I5),"In List","Not in List")
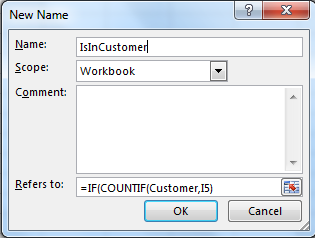
Now wherever you type ‘IsInCustomer’, It will check the value in the left cell in the Customer list.

This stops you from repeating yourself again and again.
Apply Named Ranges to Formulas
So many times, we define names to our ranges after we have already written formulas based on ranges. For example I have Total Price as Cells =E2*F2. How can we change it to Units*Unit_Cost.

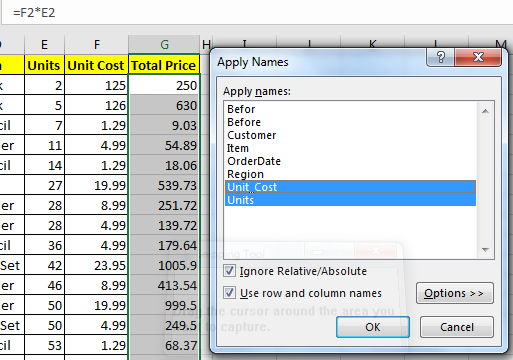
And the names are now applied. You can see it in the formula bar.

Easy to Read Formulas with Named Ranges
As you’ve seen that named ranges make it easy to read the formulas. If I write =COUNTIF(“A2:A100”,B2), no one will understand what I am trying to count, until they see the data or someone explains it to them.
But if I write =COUNTIF(region,’east’), most users will immediately get it that we are counting occurrences of ‘east’ in the region named range.
Portable Formulas
Named ranges make it very easy to copy and paste formulas without worrying about changing references. And you can take one formula from one workbook to another and it will work fine until and unless the destination workbook has the same name.
For example if you have a Formula =COUNTIF(region,east) in the Distribution Table and you have another workbook say customers that also has a named range “Region”. Now if you copy this formula directly anywhere on that workbook it will show you correct information. The structure of data will not matter. It doesn’t matter where the hell is that column in your workbook. This will work correctly.
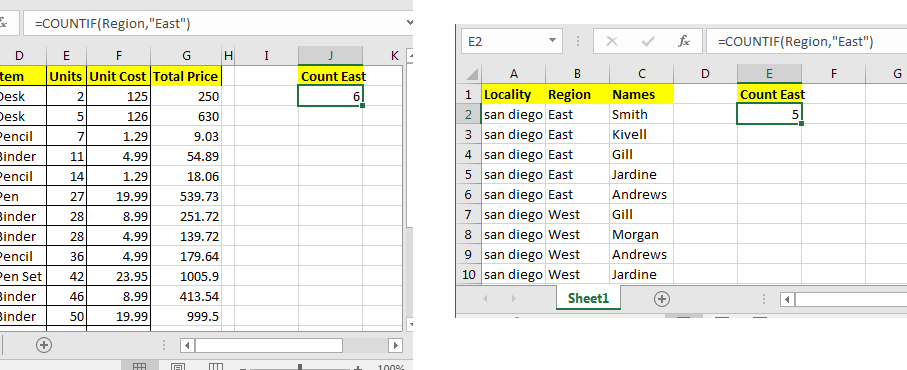
In the above image I have used the exact same formula in two different files to count the number or east occuring in the region list. Now they are in different columns but since both of them are named as regions it will work perfectly.
Navigate Easily in Workbook
It gets easier to navigate in a workbook with named ranges. You just need to type the name of the name in the name box. Excel will take you to the range, doesn’t matter where you are in the workbook. Given that named range is of Workbook scope.
For example, if you are on sheet10 and you want to get a customer list, and you don’t know on which sheet it is. Just go to name box and type ‘customer’. You’ll be directed to the named range in fraction of a second.

It will reduce the effort of remembering the ranges.
Navigate Using Hyperlinks with Named Range
When your sheet is large and you often go from one point to another, you like to use hyperlinks to navigate easily. Well Named Ranges can work perfectly with Hyperlinks. To add hyperlinks using named ranges follow these steps.
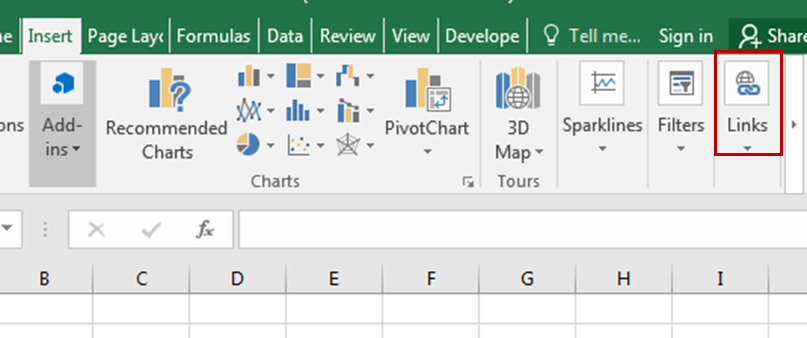
And it's done. You have your hyperlink to your chosen named range. Using this you can create an index of named ranges that you can see and click to navigate to them directly. This will make your workbook really user friendly.
Named Range and Data Validation
Named ranges and Data Validation is kind of made for each other. Named ranges make data validation highly customisable. It gets a lot easier to add a validation from a list using named range. Let us see how..
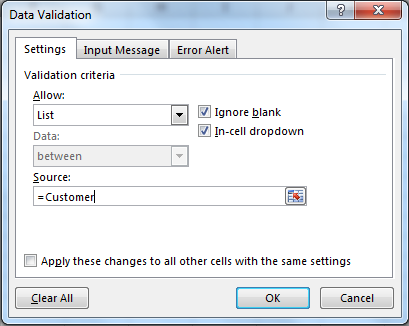
Now this cell will have names of customers who are part of the Customer named range. Easy, isn’t it.
Dependent or Cascading Data Validation with Named Ranges
Now what if you want a cascading or dependent data validation. For example, if you want a drop down list that has categories, Fruits and Vegetables. Now if you choose fruits then another dropdown should show only fruits option and if you choose Vegetable then only vegetables.
This can be easily achieved by using Named ranges. Learn how.
No Data Validation With Names of Tabled Data
Although Excel Tables provide structured names but they can not be used with data validation and Conditional Formatting. I don’t know why excel doesn’t allow it.
But it doesn’t mean that it can’t be done. You can name ranges within a table and then use them for validation. Excel does not have any problem with it.
Scope of Named Ranges
So far we talked about named ranges that had Workbook scope. What? We didn’t discuss it? Ok, so let's quickly understand what Scope of named ranges are.
What is the Scope of a Name Range?
Well scope defines where a name range can be recognised. Any name can not be recognised outside its scope. For example a name in workbook1 can not be recognised in different workbooks. Excel provides two options for scope of named ranges Worksheet and Workbook.
How to define a Scope of Named Range?
When you create a new name range, you can see a ‘Scope:’ section. Click on the drop down and choose the scope for your name range. You can’t change scope once you have created a named range. So better do it before. By default, it is a workbook.

Hope this article about How to create a Table and name the table in Excel is explanatory. Find more articles on calculating values and related Excel formulas here. If you liked our blogs, share it with your friends on Facebook. And also you can follow us on Twitter and Facebook. We would love to hear from you, do let us know how we can improve, complement or innovate our work and make it better for you. Write to us at info@exceltip.com.
Related Articles :
How to use the Shortcut To Toggle Between Absolute and Relative References in Excel : F4 shortcut to convert absolute to relative reference and same shortcut use for vice versa in Excel.
How to use Shortcut Keys for Merge and Center in Excel : Use Alt and then follow h, m and c to Merge and centre cells in Excel.
How to Select Entire Column and Row Using Keyboard Shortcuts in Excel : Use Ctrl + Space to select whole column and Shift + Space to select whole row using keyboard shortcut in Excel
Paste Special Shortcut in Mac and Windows : In windows, the keyboard shortcut for paste special is Ctrl + Alt + V. Whereas in Mac, use Ctrl + COMMAND + V key combination to open the paste special dialog in Excel.
How to Insert Row Shortcut in Excel : Use Ctrl + Shift + = to open the Insert dialog box where you can insert row, column or cells in Excel.
Popular Articles :
How to use the IF Function in Excel : The IF statement in Excel checks the condition and returns a specific value if the condition is TRUE or returns another specific value if FALSE.
How to use the VLOOKUP Function in Excel : This is one of the most used and popular functions of excel that is used to lookup value from different ranges and sheets.
How to use the SUMIF Function in Excel : This is another dashboard essential function. This helps you sum up values on specific conditions.
How to use the COUNTIF Function in Excel : Count values with conditions using this amazing function. You don't need to filter your data to count specific values. Countif function is essential to prepare your dashboard.
The applications/code on this site are distributed as is and without warranties or liability. In no event shall the owner of the copyrights, or the authors of the applications/code be liable for any loss of profit, any problems or any damage resulting from the use or evaluation of the applications/code.